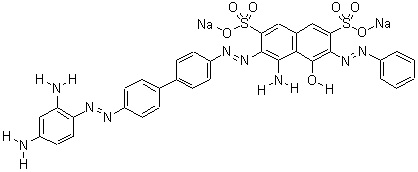
Figure 1

Figure 1

Figure 2 SEM images of (a)TiO2 and (b) Zeolite Y-Supported TiO2 (1.0 cm = 0.83 m).
Figure 3 Elemental Analysis of (a) Na-Y Zeolite and (b) Zeolite Y-Supported TiO2
Figure 4 Chlorazol E Dye Degradation Profiles at pH 2, 6, and 11.
Figure 5 Chlorazol E Dye Degradation Profiles at Concentrations from 6 to 30 ppm.
Figure 6 Chlorazol E Dye Degradation Profiles from 30 to 70 oC.
Figure 7 Semilog Plot of Chlorazol E Dye Concentration (ppm) with Time (minutes).
pH |
Before Treatment |
After Treatment |
2 |
16 mg/l |
20 mg/l |
6 |
18.5 mg/l |
10 mg/l |
11 |
13.8mg/l |
10.8 mg/l |
Table 1 COD Measurements for Dye Solutions at pH 2,6, and 11 Before and After Chlorazol E Degradation.
pH |
Before Degradation |
After Degradation |
|
|
|
2 |
52.36mS/cm |
3309mS/cm |
|
|
|
6 |
16.31mS/cm |
288mS/cm |
|
|
|
11 |
4427mS/cm |
170mS/cm |
|
|
|
Table 2 Conductivity Measurement of Dye Solutions at pH 2, 6, 11 Before and After Chlorazol E Degradation.
Initial concentration |
k (min –1) |
R 2 |
10 ppm |
0.0023 |
0.8572 |
16 ppm |
0.0018 |
0.9789 |
30 ppm |
0.001 |
0.9592 |
Initial pH |
k (min –1) |
r2 |
pH 6 |
0.0014 |
0.9428 |
pH 11 |
0.0013 |
0.9947 |
Table 3Kinetics of Chlorazol E Photodegradation at Different Concentrations and pH.