General Molecular Structure of Covalent Gemcitabine and Epirubicin Immunochemotherapeutics
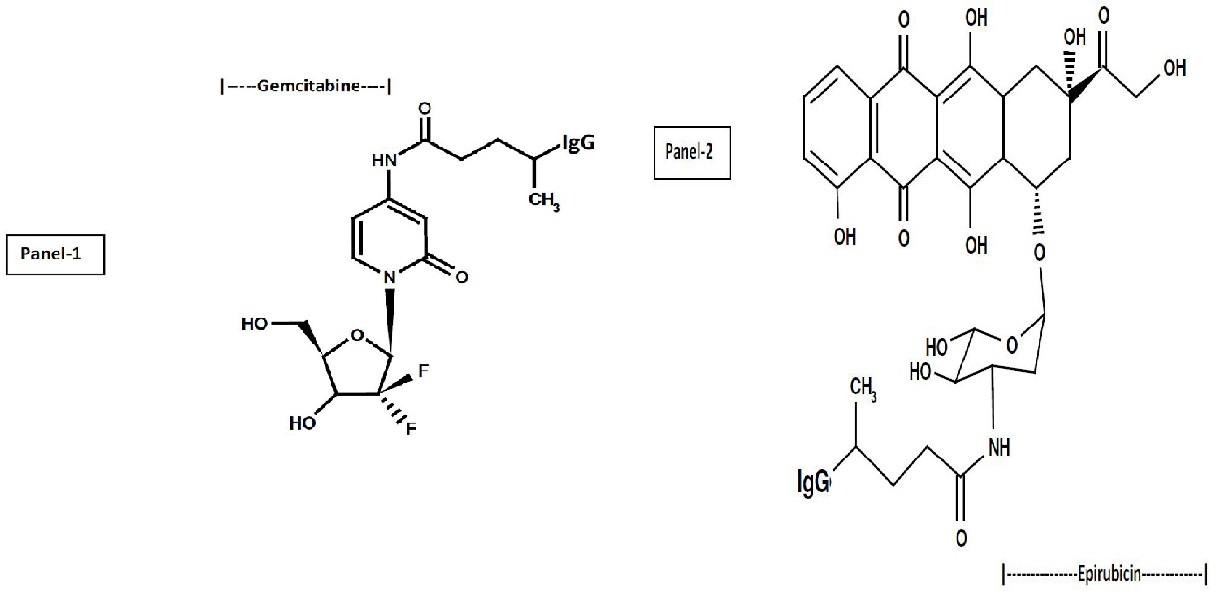
Figure 1 Molecular design and chemical composition of covalent gemcitabine and epirubicin immunochemotherapeutics. Legends: (Panel 1) gemcitabine-(C4-amide)-[anti-EGFR]; and (Panel 2) epirubicin-(C3-amide)-[anti-HER2/neu]. Both covalent immunochemotherapeutics were synthesized utilizing a 2-stage organic chemistry reaction scheme that initially produces a chemotherapeutic analog that is a UV-photoactivated intermediate. Covalent bonds are formed at the monoamine groups of gemcitabine or epirubicin and the side chains of amino acid residues within the sequence of immunoglobulin fractions.