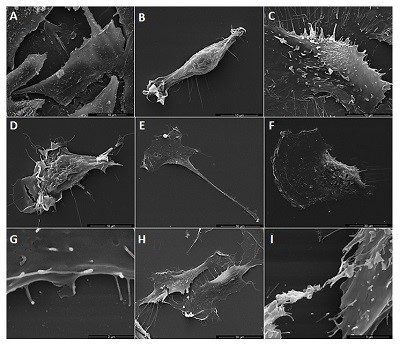
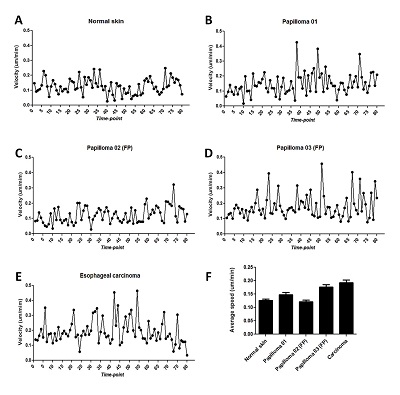
|
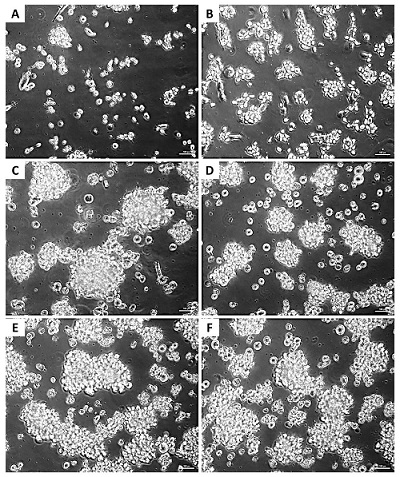
Passage 1 |
Passage 2 |
Passage 3 |
Passage 4 |
|
Passage 5 |
Passage 6 |
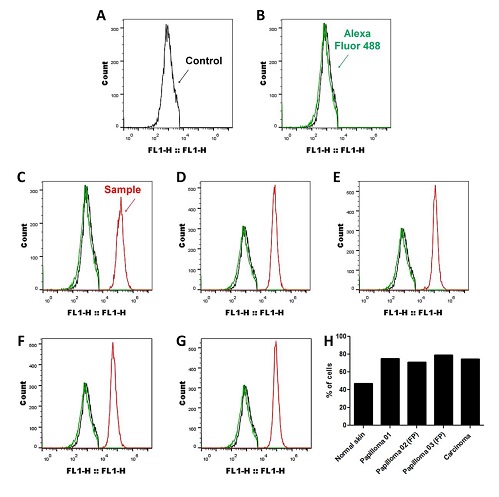
Normal skin |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Papilloma 01 |
BPV-1 |
BPV-1 and 2 |
BPV-2 |
BPV-1 and 2 |
|
BPV-1 and 2 |
- |
Papilloma 02 |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-2 and 4 |
BPV-1 and 2 |
|
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-2 and 4 |
Papilloma 03 |
BPV-2 and 4 |
BPV-1 and 2 |
BPV-2 |
BPV-2 and 4 |
|
BPV-1 and 2 |
BPV-2 |
Carcinoma |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
|
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
BPV-1, 2 and 4 |
Table1 BPV types identified in primary cell cultures
Results based on Araldi et al. [7]
|
Multiple comparison |
Mean Difference |
q |
P< 0.05 |
|
Normal skin and papilloma 01 |
-0.02171 |
2.818 |
No |
|
Normal skin and papilloma 02 (FP) |
0.004682 |
0.608 |
No |
|
Normal skin and papilloma 03 (FP) |
-0.04973 |
6.457 |
Yes |
|
Normal skin and esophageal carcinoma |
-0.06675 |
8.666 |
Yes |
|
Papilloma 01 and Papilloma 02 (FP) |
0.02639 |
3.426 |
No |
|
Papilloma 01 and Papilloma 03 (FP) |
-0.02803 |
3.639 |
No |
|
Papilloma 01 and esophageal carcinoma |
-0.04504 |
5.848 |
Yes |
|
Papilloma 02 (FP) and papilloma 03 (FP) |
-0.05441 |
7.065 |
Yes |
|
Papilloma 02 (FP) and esophageal carcinoma |
-0.07143 |
9.274 |
Yes |
|
Papilloma 03 (FP) and esophageal carcinoma |
-0.01702 |
2.209 |
No |
Table 2Result of Tukey’s multiple comparison test
FP - fibropapilloma