One-way analysis of variance |
|
|
|
P value |
0.662 |
|
|
P value summary |
ns |
|
|
Are means significantly different? (P < 0.05) |
No |
|
|
Number of groups |
3 |
|
|
F |
0.4132 |
|
|
R squared |
0.003432 |
|
|
Bartlett's test for equal variances |
|
|
|
Bartlett's statistic (corrected) |
2.151 |
|
|
P value |
0.3411 |
|
|
P value summary |
ns |
|
|
Do the variances differ signif. (P < 0.05) |
No |
|
|
ANOVA Table |
SS |
df |
MS |
Treatment (between columns) |
10.78 |
2 |
5.388 |
Residual (within columns) |
3129 |
240 |
13.04 |
Total |
3140 |
242 |
|
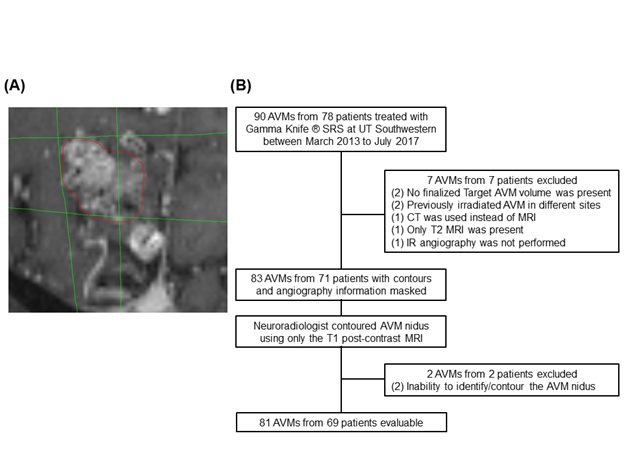
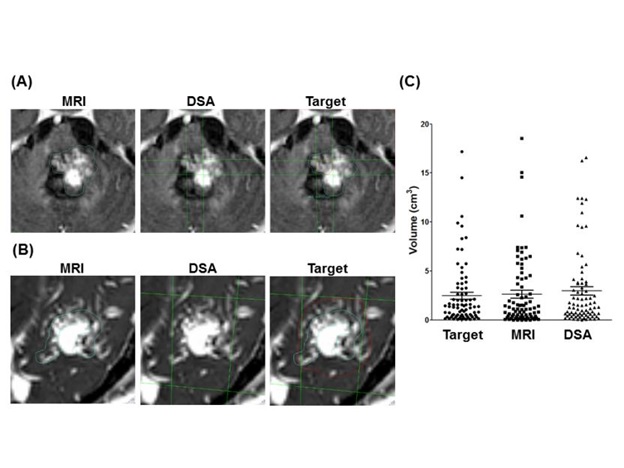
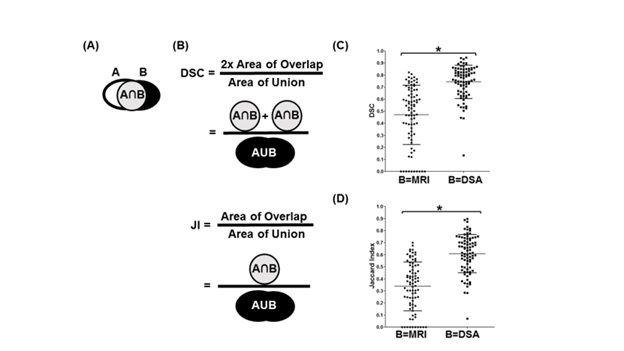
Table 1:One-way ANOVA comparison of the target, MRI-generated and DSA-generated volumes
Table Analyzed: DSC |
Target:MRI |
Target:DSA |
Number of values |
81 |
81 |
Minimum |
0 |
0.1327 |
25% Percentile |
0.3129 |
0.6613 |
Median |
0.5297 |
0.7763 |
75% Percentile |
0.6778 |
0.8467 |
Maximum |
0.824 |
0.9456 |
Mean |
0.4702 |
0.7437 |
Std. Deviation |
0.2465 |
0.1377 |
Std. Error |
0.02739 |
0.0153 |
Lower 95% CI |
0.4157 |
0.7133 |
Upper 95% CI |
0.5247 |
0.7742 |
Paired t test |
|
|
P value |
< 0.0001 |
|
Are means signif. different? (P < 0.05) |
Yes |
|
One- or two-tailed P value? |
Two-tailed |
|
t, df |
t=8.260 df=80 |
|
Number of pairs |
81 |
|
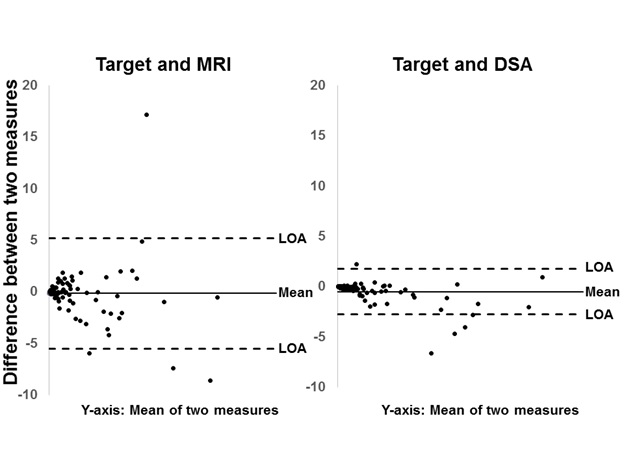
Table 2:Matched pair analysis of Dice Similarity Coefficients(DSC) between the finalized target and DSA-generated volume compared to DSC between the finalized target and the MRI-generated volume.
Table Analyzed: Jaccard Index |
Target:MRI |
Target:DSA |
Number of values |
81 |
81 |
Minimum |
0 |
0.07106 |
25% Percentile |
0.1854 |
0.494 |
Median |
0.3603 |
0.6344 |
75% Percentile |
0.5127 |
0.7342 |
Maximum |
0.7007 |
0.8969 |
Mean |
0.3391 |
0.609 |
Std. Deviation |
0.202 |
0.159 |
Std. Error |
0.02245 |
0.01766 |
Lower 95% CI |
0.2945 |
0.5738 |
Upper 95% CI |
0.3838 |
0.6441 |
Paired t test |
|
|
P value |
< 0.0001 |
|
Are means signif. different? (P < 0.05) |
Yes |
|
One- or two-tailed P value? |
Two-tailed |
|
t, df |
t=9.519 df=80 |
|
Number of pairs |
81 |
|
Table 3:Matched pair analysis of Jaccard Index between the finalized target and DSA-generated volume compared to DSC between the finalized target and the MRI-generated volume.