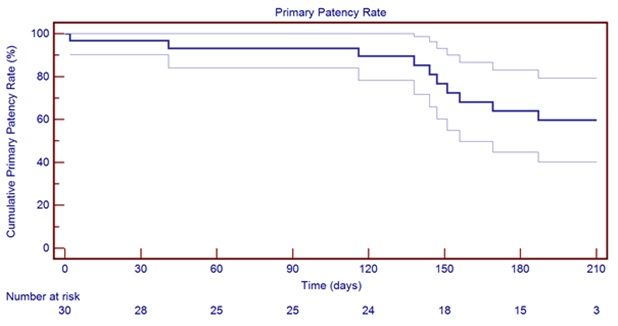
Graph 1 6-month primary patency rate

Graph 1 6-month primary patency rate
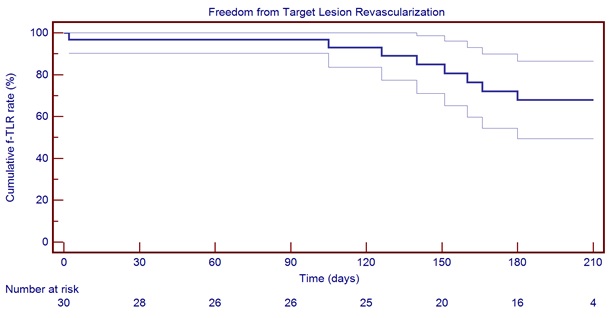
Graph 2 6-month freedom from Target Lesion Revascularization
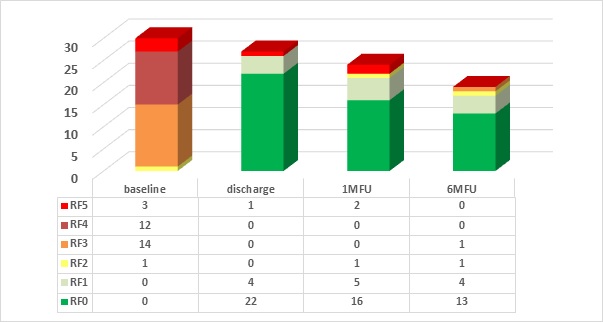
Graph 3 Evolution in Rutherford Classification
|
|
Findings |
Doppler signals |
||
Category |
Description / prognosis |
Sensory loss |
Muscle weakness |
Arterial |
Venous |
I. Viable |
Not immediately threatened |
None |
None |
Audible |
Audible |
II. Threatened |
Salvageable if promptly treated |
Minimal (toes) or none |
None |
Inaudible |
Audible |
b. Immediately |
Salvageable with immediate revascularization |
More than toes, associated with rest pain |
Mild, moderate |
Inaudible |
Audible |
III. Irreversible |
Major tissue loss or permanent nerve damage inevitables |
Profound, anesthetic |
Profound, paralysis (rigor) |
Inaudible |
Inaudible |
Table 1 : Clinical categories of acute limb ischemia
1. |
Patient is willing to comply with specified follow-up evaluations at the specified times |
2. |
Patient is >18 years old |
3. |
Patient understands the nature of the procedure and provides written informed consent, prior to enrolment in the study |
4. |
Patient has a projected life-expectancy of at least 6 months |
5. |
Symptomatic acute or subacute stent or bypass occlusion in the femoropopliteal artery |
6. |
Target vessel diameter ≥ 3 mm and ≤ 8 mm |
7. |
Patient is candidate for thrombolytic or anticoagulation medication |
8. |
Patient is able and willing to comply with study follow-up requirements |
Table 2 : Inclusion criteria
1. |
No patent artery until the foot |
2. |
Inability of crossing lesion with guidewire |
3. |
Known active infection at the time of intervention |
4. |
Untreated flow-limiting inflow lesions |
5. |
Perioperative unsuccessful ipsilateral percutaneous vascular procedure to treat inflow disease just prior to enrolment |
6. |
Aneurysm in the target vessel |
7. |
Severe medical comorbidities (untreated CAD/CHF, severe COPD, metastatic malignancy, dementia, etc) or other medical condition that would preclude compliance with the study protocol |
8. |
Major distal amputation (above the transmetatarsal) in the study limb or non-study limb |
9. |
Septicemia or bacteremia |
10. |
Any previously known coagulation disorder, including hypercoagulability |
11. |
Contraindication to anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy |
12. |
Patient with known hypersensitivity to heparin, including those patients who have had a previous incidence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) type II |
13. |
Currently participating in another clinical research trial |
14. |
The patient must be excluded in case any of the contraindications as listed in the IFU is present |
Table 3: Exclusion criteria
Age (min-max; ±SD) (years) |
71.24 (51.75-87.33 ± 9.39) |
Gender (%) -Male -Female |
23 (76.67%) 7 (23.33%) |
Nicotine abuse -Never -Former -Current |
6 (20.00%) 8 (26.67%) 16 (53.33%) |
Hypertension -Yes, medicated -Yes, not medicated -No |
20 (66.67%) 2 (6.67%) 8 (26.67%) |
Diabetes -Yes, type I -Yes, type II -No |
5 (16.67%) 5 (16.67%) 20 (66.67%) |
Renal insufficiency -Yes, on dialysis -Yes, not on dialysis -No |
2 (6.67%) 2 (6.67%) 26 (86.67%) |
Hypercholesterolemia -Yes -No |
21 (70.00%) 9 (30.00%) |
Obesity -Yes -No |
9 (30.00%) 21 (70.00%) |
History of coronary intervention -Yes -No |
8 (26.67%) |
History of cerebrovascular intervention -Yes -No |
5 (16.67%) 25 (83.33%) |
Rutherford 2 |
1 (3.33%) |
Rutherford 3 |
14 (46.67%) |
Rutherford 4 |
12 (40.00%) |
Rutherford 5 |
3 (10.00%) |
Table 4 : Patient demographics
Lesion side (N=30) -Left (%) -Right (%) |
19 (63.33%) 11 (36.67%) |
Lesion Type -Stenosis -Occlusion |
0 (0.00%) 30 (100.00%) |
Lesion length (min-max; ±SD) (mm) |
170.5(15.0-500; ± 146.29) |
Proximal reference vessel diameter (min-max; ±SD) (mm) |
5.43 (4.0-7.0; ± 0.63) |
Presence of calcification (%) |
6(20.00%) |
Presence of dissection (%) |
1(3.33%) |
Presence of thrombus (%) |
22 (73.33%) |
Presence of ulceration (%) |
1 (3.33%) |
Table 5: Lesion characteristics