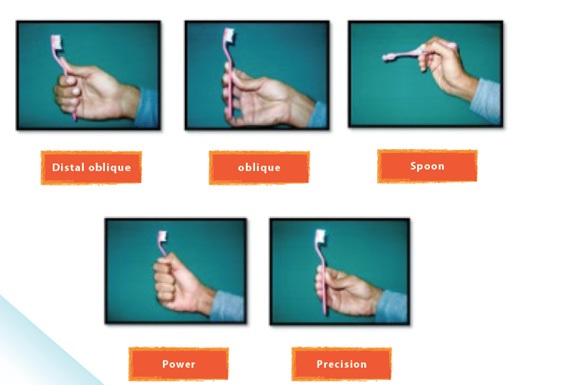
Figure 1 Different types of tooth brush grip described by Beals et al

Figure 1 Different types of tooth brush grip described by Beals et al
Table 1: Frequency distribution of volunteers |
||
Grip |
||
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Distal oblique |
22 |
55.0 |
Oblique |
11 |
27.5 |
Precision |
7 |
17.5 |
Total |
40 |
100.0 |
Brushing method visits 1 and 2 |
||
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Horizontal |
23 |
57.5 |
Vertical |
8 |
20.0 |
Circular |
9 |
22.5 |
Total |
40 |
100.0 |
Table 2: Frequency distribution of subjects |
||
Grip |
||
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Distal oblique |
22 |
55.0 |
Oblique |
11 |
27.5 |
Precision |
7 |
17.5 |
Total |
40 |
100.0 |
Brushing Technique visits 3,4 and 5 |
||
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Modified Bass |
20 |
50.0 |
Modified Stillman's |
20 |
50.0 |
Total |
40 |
100.0 |
Table 3:Comparison of the effects of three grips on plaque index |
|||||||
|
|
PRE-1 |
PRE-5 |
sig. 2 TAILED |
POST-1 |
POST-5 |
sig. 2 TAILED |
GRIP |
DISTAL OBLIQUE |
173.00 ± 52.74 |
159.30 ± 48.64 |
NS |
168.50 ± 45.00 |
13.95 ± 10.67 |
S |
OBLIQUE |
180.00 ± 49.37 |
168.18 ± 19.11 |
NS |
93.64 ± 25.30 |
16.45 ± 9.68 |
S |
|
PRECISION |
154.00 ± 33.50 |
124.57 ± 45.98 |
NS |
70.71 ± 37.88 |
6.57 ± 3.73 |
S |
|
Confidence interval was evaluated at 95%; significance p < 0.05; S=Significant; NS-not significant |
|||||||
Table 4: Comparison of the effects of two brushing techniques on plaque scores |
|||||||
|
|
PRE-3 |
PRE-5 |
sig. 2 TAILED |
POST-3 |
POST-5 |
sig. 2 TAILED |
BRUSHING TECHNIQUE |
MBT |
185.25 ± 33.83 |
143.25 ± 43.81 |
S |
40.35 ± 26.41 |
17.05 ± 11.63 |
S |
MST |
183.80 ± 39.93 |
168.15 ± 41.13 |
S |
45.85 ± 21.28 |
9.65 ± 6.20 |
S |
|
MBT: modified Bass technique; MST: modified Stillman’s technique |
|||||||
Table 5: Comparison of the combined effects of brushing techniques and grips on plaque removal |
|||||||
|
MBT |
MST |
|||||
PRE-3 |
PRE-5 |
sig. 2 TAILED |
PRE-3 |
PRE-5 |
sig. 2 TAILED |
||
GRIP |
DISTAL OBLIQUE |
183.11 ± 37.83 |
138.22 ± 50.87 |
S |
185.69 ± 40.60 |
174.00 ± 42.98 |
NS |
OBLIQUE |
192.62 ± 23.12 |
165.38 ± 12.17 |
S |
184.00 ± 37.32 |
175.67 ± 34.53 |
NS |
|
PRECISION |
172.00 ± 52.67 |
99.33 ± 48.95 |
NS |
177.50 ± 50.07 |
143.50 ± 38.95 |
NS |
|
MBT: modified Bass technique; MST: modified Stillman’s technique |
|||||||