Microscopy in Forensic Odontology: Scope and Applications
Received Date: December 05, 2022 Accepted Date: January 15, 2023 Published Date: January 19, 2023
doi: 10.17303/jfrcs.2023.8.101
Citation: Asnani Piyush S, Ali Shireen M, Odedra Sima P, Paghadal Harita (2023) Microscopy in Forensic Odontology: Scope and Applications J Forensic Res Crime Stud
Abstract
A milestone in the world of science, microscope has revolutionized the field of modern forensics. Over the years the field of microscopy has come a long way and has paved ways for newer techniques of evaluation of evidences from various scenarios like natural disasters, criminal cases, suicidal cases etc. which if done conventionally might be missed by naked eyes of the investigator. It plays an inevitable role in examination of soil, dust, fibres, hair or other trace material by forensic scientist, study of genome by forensic epidemiologist, analysis of DNA by a geneticists and evaluation of soil, water, any building component, bullets found at the crime scene. Here too, the microscopes are of great help in several domains like in comparison of dental structures, in age estimation that applies the histologic methods, examination of various evidences collected from the crime scene, etc. Conventional microscopic techniques involve transmitted-light, absorption microscopy which is appropriate for coloured objects of resolvable size, and instrumentally is the simplest form of microscopy. Colourless, transparent objects can be studied only by retardation techniques (polarization, phase-contrast, interference; these techniques depend upon conversion of phase retardation which leads to changes in intensity of light that can be seen by the eye. Hence these evolving techniques in microscopy add value and precision in evidence collection and evaluation. The present review article is prepared with an aim to compile and highlight the applications of several range of microscopes under forensic odontology perspective. This review article may be a used as a ready reference to apply the microscopic techniques in investigations dealing with dental exhibits.
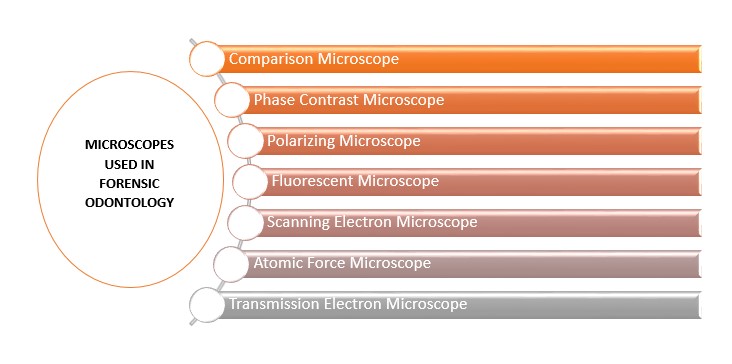
Keywords: Microscopes; Forensic Odontology; Stereomicroscope; Scanning Electron Microscope; Phase Contrast Microscope; Comparison Microscope
Introduction
Forensic Science is a multidisciplinary, multi- dimensional specialty which deals with the application of almost all branches of science under legal context. The teeth being the hardest and the strongest substance in human body, have the potential to resist environmental, thermal and taphonomic changes and can therefore be considered as one of the most reliable and well-grounded form of evidences, especially in forensic human iden- tification cases [1]. The developing dentition provides a valuable information related to the age of individual right from the intrauterine life till adolescent. As the maxilla, mandible grows along with development of tooth, various modifications occur over the years at different stages of growth & development which can be monitored and employed as a guide for identification of age, sex, ethnicity, cause of death & identification of victim and suspect etc. in the civil and criminal judicial system. So, the evidences from oral and maxillofacial region can play a vital role in human identification in case of mass disasters, domestic violence and child abuse cases. Microscopes are compound to complex instruments consisting of optical lenses, illumination, mirrors and other supporting system that helps in magnifying the tissue or object, revealing the fine details which cannot be perceived by naked human eye. The purpose of using microscope is to obtain detailed information about the morphology, size, texture, structure, chemical constituent and electrical properties of the samples or objects [2-4]. Understanding of these minute details seen under the microscope can widen the scope of identification of human remains.
Conclusion
This article serves as a ready reckoner for illuminating the utility of different types of microscopes in the field of Forensic Odontology. This article summarizes the mechanism of action of compound and other advanced microscopes, along with their abilities to evaluate and analyze characteristic features from oral and maxillofacial evidences in estimating the age, sex, race, comparing ante-mortem and post-mortem evidences and determining the type of accident or crime.
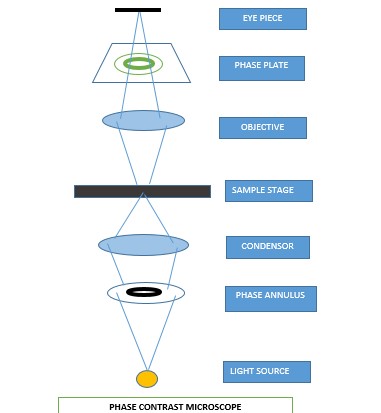
- Priya Shirish Joshi, Madhuri S. Chougule, Gaurav Pralhad Agrawal (2015) Comparison of polarizing & phase contrast microscopy for estimation of age based on cemental annulations
- Metcalf RD, Klim-Lemann J (2015) Overview of Forensic Odontology. J Calif Dent Assoc.
- Thakur P (2023) “Applications of microscope in different fields of forensic science” International Journal of Advance Research and innovative ideas in education.
- Lister G. Clark (2009) Forensic applications of Microscopy. Australian journal of forensic science.
- Pradeep L, Kokila G, Gopinathan PA, Guruswamy S, Nazir SH et al. (2021) Age estimation with cemental annulation using light, phase contrast and polarized microscopy. J Microsc Ultrastruct.
- Jasbir Arora, Indu Talwar, Daisy Sahni, Vidya Rattan (2016) Secondary dentine as a sole parameter for age estimation: Comparison and reliability of qualitative and quantitative methods among North Western adult Indians,Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences 6: 170-8.
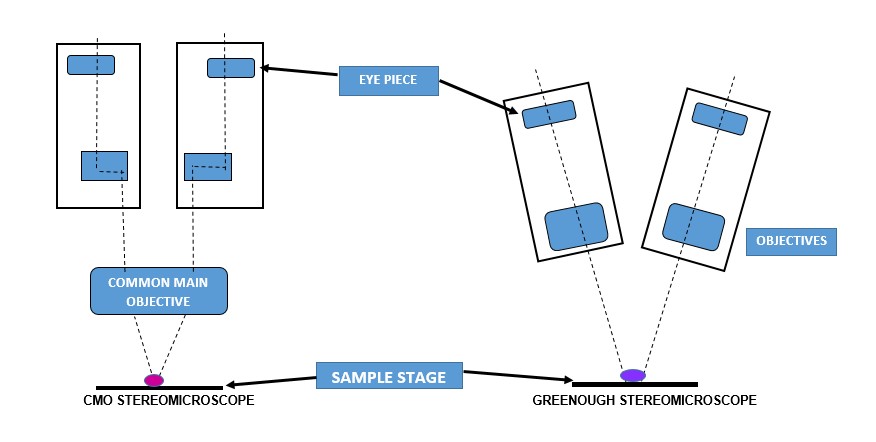
- Narayan V. Keerthi et al. (2017) "Stereomicroscopic study on unsectioned extracted teeth." Journal of Forensic Dental Sciences.
- https://www.smacgigworld.com/blog/dark-field- and-phase-contrast-microscopes.php
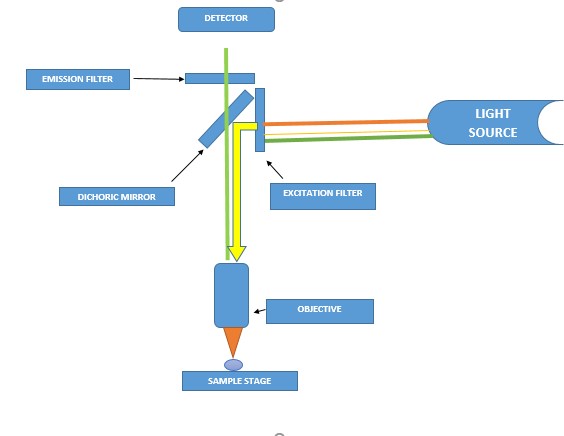
- Nayar A, Singh HP, Leekha S (2014) Pulp tissue in sex determination: A fluorescent microscopic study. J Forensic Dent Sci.
- Kalistu, Siritta, Doggalli, D Nagabhushana (2016) Gender Determination by Forensic Odontologist: A Review of various methods 15: 78-85.
- Jeddy N, Ravi S, Radhika T (2017) Current trends in forensic odontology. J Forensic Dent Sci.
- Selvan CT, Malkovskiy AV, Vijayaraghavan R, Babu GR, Senthilkumar S (2019) New insights into odontological exploration of drowning using rat model-A pilot study. The Journal of Forensic Odonto-stomatology.
- Gupta V, Kaur A (2021) Palatal rugoscopy as an adjunct for sex determination in forensic odontology (Sri Ganganagar population): A cross-sectional study of 100 subjects. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 25: 556.
- Ma XF, Jin M, Sun H, Mi CB (2020) Application Status and Prospect of Bite Mark Evidence in Forensic Odontology. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 36: 369-73.
- Dinkar D, Siddarth P, Shravya M, Kishore B, Nayak SV et al. (2018) Ameloglyphics- A Mirror within You. Austin J Forensic Sci Criminol.
- Lakshya R, Dr Gheena (2021) “Tongue prints in forensic odontology - a review” 6.
- Porter AE, Nalla RK, Minor A, Jinschek JR, Kisielowski C et al. (2005) A transmission electron microscopy study of mineralization in age-induced transparent dentin. Biomaterials 26: 7650-60.
- Mahija Janardhanan, B Umedeahan, S Rakesh “Neonatal line as a linear evidence of live birth: Estimation of postnatal survival of a new born from primary tooth germs” J Forensic Dent Sci
- Chakraborty I, Chakrabarti S, Managuli V, Mazumder N (2022) Atomic Force Microscopy Study of Diatoms. In Diatom Microscopy (eds N. Mazumder and R. Gordon).
- Manish S, Devinder S “Use of Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) in Forensic Entomology” International journal of science and advance Research in technology.
- https://www.microscopeworld.com/p-3358-food- analysis-under-the-microscope.aspx#:~:text=More%20 extensive%20food%20analysis%20is%20performed%20 with%20a,microscope%20is%20invaluable%20for%20 examining%20such%20crystalline%20substances.
- Barbara P. Wheeler, Lori J Wilson (2008) Practical Forensic Microscopy: A Laboratory Manual
- Rothwell BR (2001) Principles of dental identification. Dent Clin North Am.
- Pretty IA (2007) Forensic dentistry: 1. Identification of human remains. Dent Update.
- Nuzzolese E (2018) Dental autopsy for the identification of missing persons. J Forensic Dent Sci.
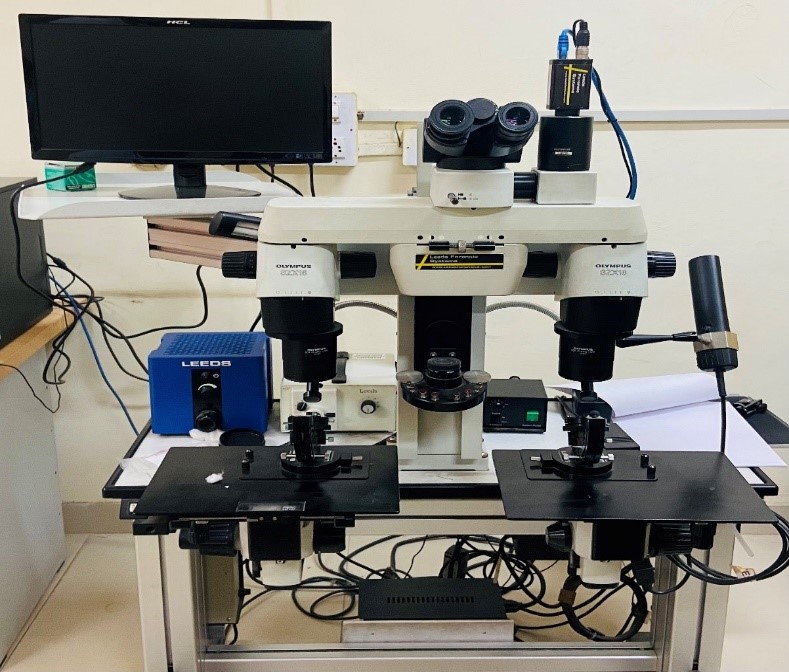

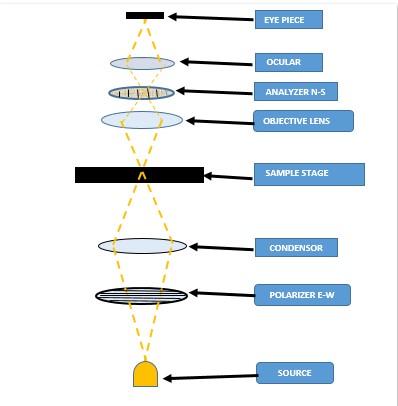

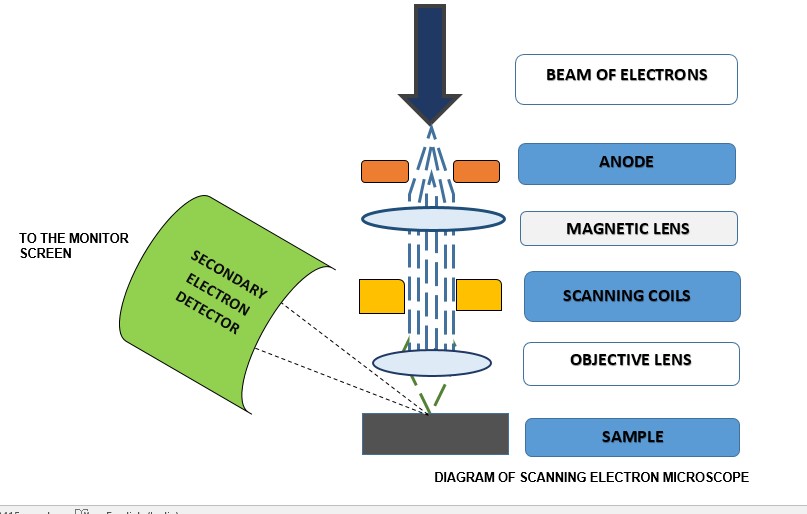
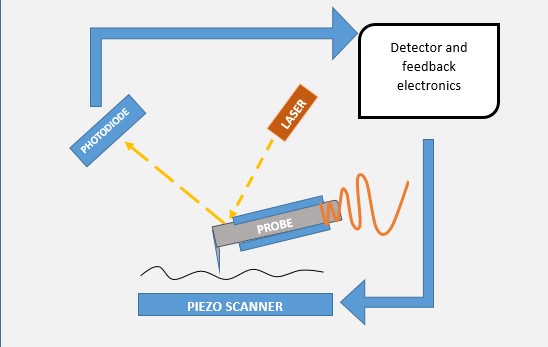
Tables at a glance
Figures at a glance