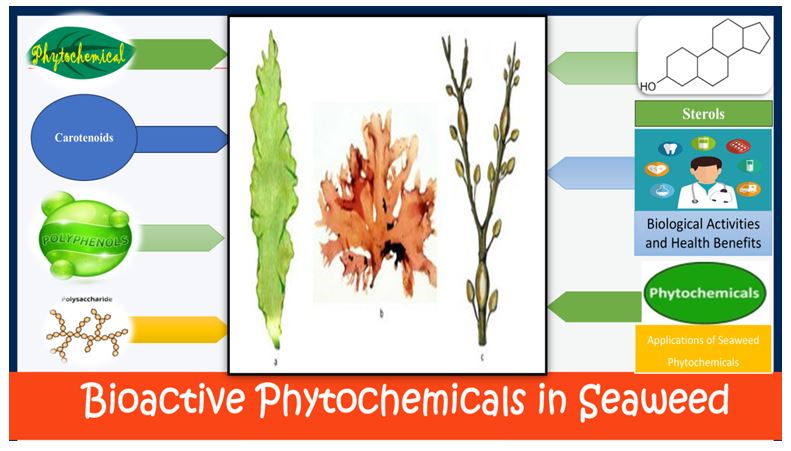
Figure 1: An illustration of the different bioactive phytochemicals present in the seaweeds
| Sr. No. | Name of Seaweed | Isolated Bioactive Compounds | Effect and Potential |
| 1 | Laminaria japonica | Fucoxanthins | Antitumoral activity on lung cancer cells |
| 2 | Colpomenia sinuosa, Sargassum prismaticum | Fucoxanthins | Antitumoral activity on lung cancer cells |
| 3 | Undaria pinnatifida | Fucoxanthins | Antitumoral activity on SiHa, Malme-3M cells |
| 4 | Cladosiphon okamuranus | Fucoxanthins | Antimicrobial activity |
| 5 | Laminaria japonica | Fucoxanthins | Antimicrobial activity |
| 6 | Fucus vesiculosus | Fucoxanthins | Antimicrobial activity |
| 7 | Fucus evanescens | Fucoxanthins | Antiviral activity against ECHO-1, HIV-1, HSV-1, HSV-2 |
| 8 | Sargassum patens | Sulfate polysaccharide | Antiviral activity against HSV-1, HSV-2 |
| 9 | Gracilaria lemaneiformis | Sulfate polysaccharide | Anti-obesity, antidiabetic activities |
| 10 | Ecklonia cava | Phloroglucinol | Anti-inflammatory activity |
| 11 | Padina tetrastromatica | Carrageenan | Anti-inflammation |
| 12 | Ulva sp. | Ulvans | Anti-aging |
| 13 | Laminaria japonica | Laminaran | Antioxidant activity |
Table 1: A list of the different bioactive compounds of seaweed and their therapeutic potential
| Sr. no. | Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1 | Conventional Extraction | The method has been tested initially. | Long extraction time, using a lot of solvents, acids and bases resulted in the degradation of polysaccharide |
| 2 | Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE) | Short extraction time with a relatively small amount of solvent. | High heat causes the degradation of polyphenols. |
| 3 | Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE) | The extraction time is short. The method works at low temperatures using a relatively little solvent. | Degradation and changes in the structure of polysaccharides. |
| 4 | Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) | CO was removed from the extract easily and did not cause structural degradation of the compound. | High pressure to retain solvent which hurts the compound. |
| 5 | Pressurized Solvent Extraction (PSE) | The method is similar to Soxhlet extraction, but the solvent has high extraction properties. | The combination of high temperature and pressure to increase the solubility and diffusion of the solvent is difficult. |
| 6 | Enzyme-Assisted Extraction (EAE) | Does not use organic solvents but high yield. Extraction results depend on the time, pH, and enzyme temperature. Efficiency depends on the nature of the enzyme. | Does not use organic solvents but high yield. Extraction results depend on the time, pH, and enzyme temperature. Efficiency depends on the nature of the enzyme. |
Table 2: depicts the various extraction processes of phytochemicals from seaweeds along with their pros and cons

Figure 1: An illustration of the different bioactive phytochemicals present in the seaweeds
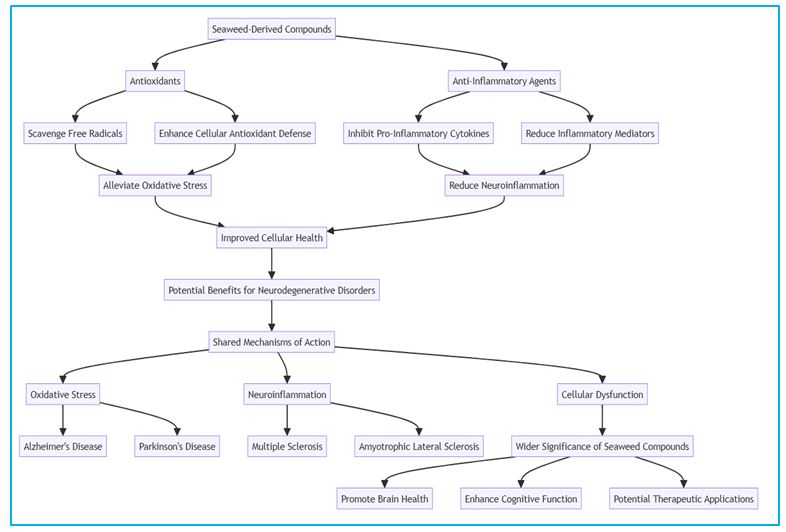
Figure 2: Shows the wider significance of the compounds derived from seaweed
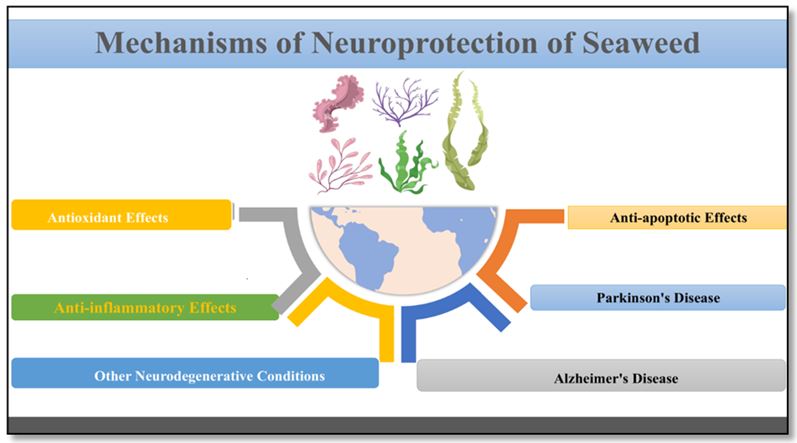
Figure 3: Neuroprotective potential of seaweeds
Tables at a glance
Figures at a glance