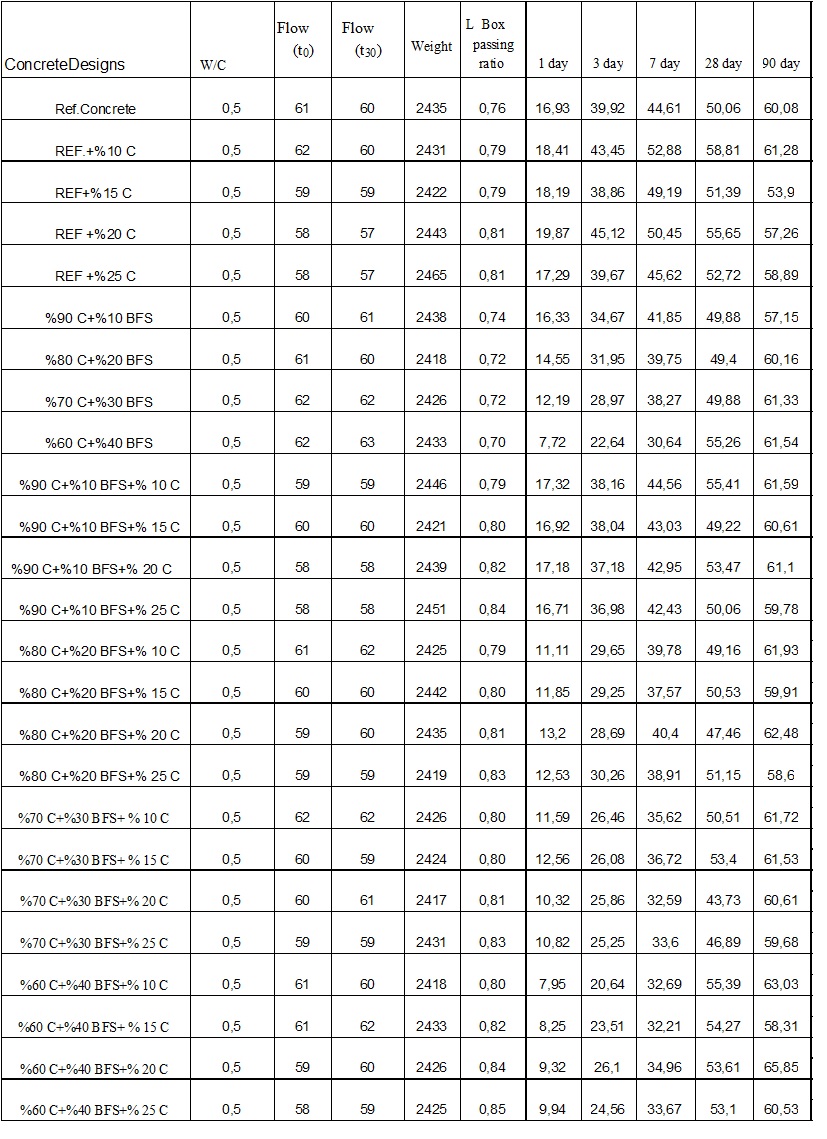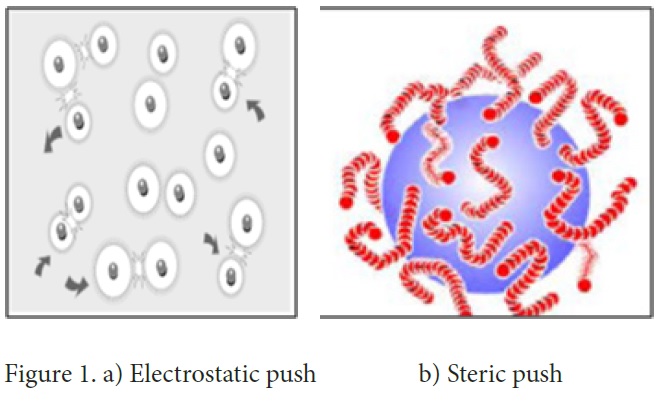
Figure 1

Figure 1
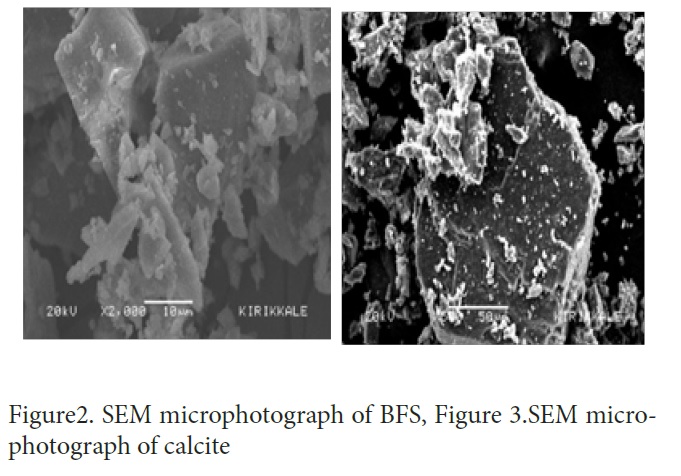

Figure 2
Figure 3
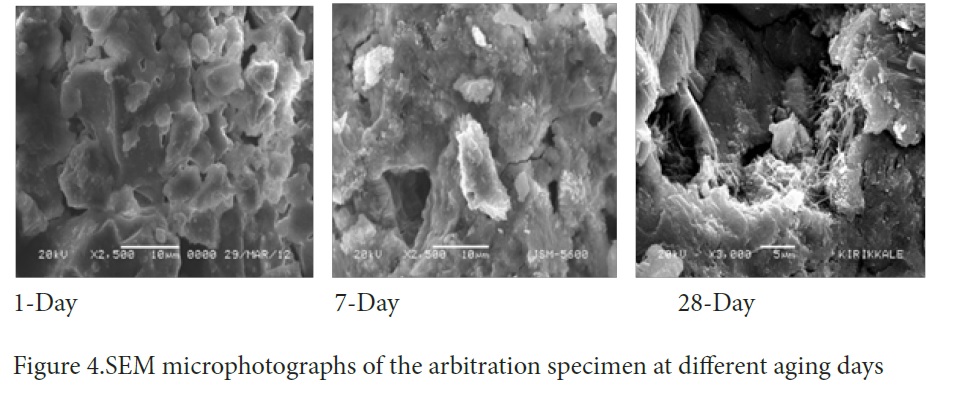
Figure 4
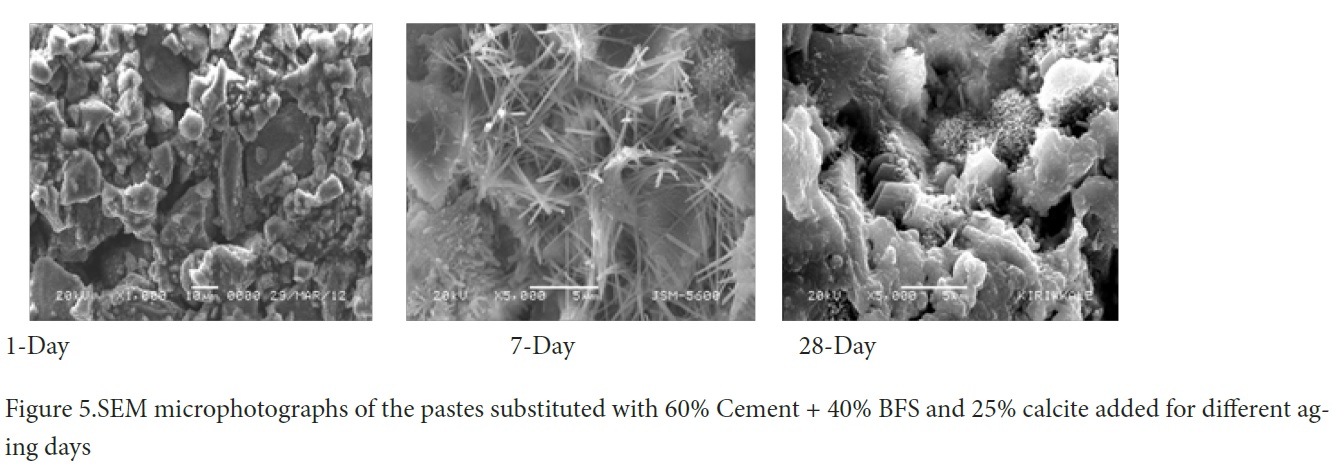

Figure 5
Figure 6
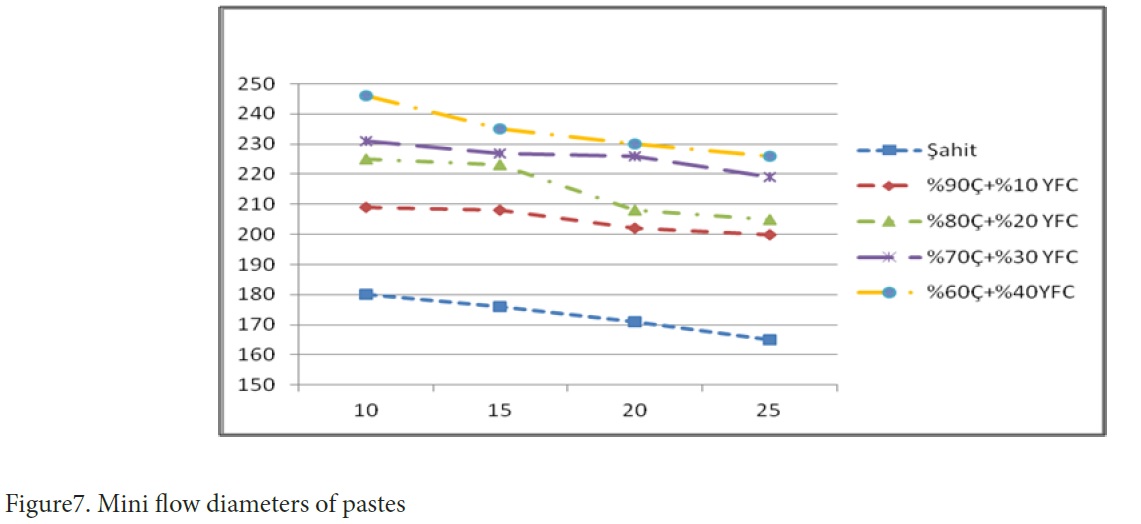
Figure 7
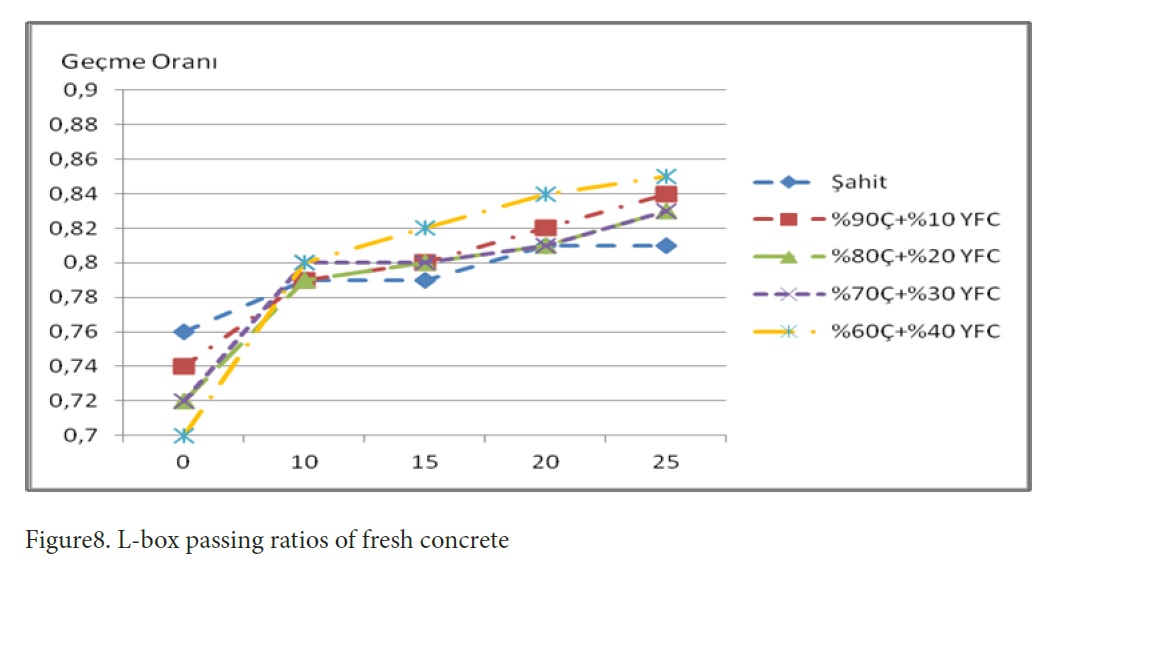
Figure 8
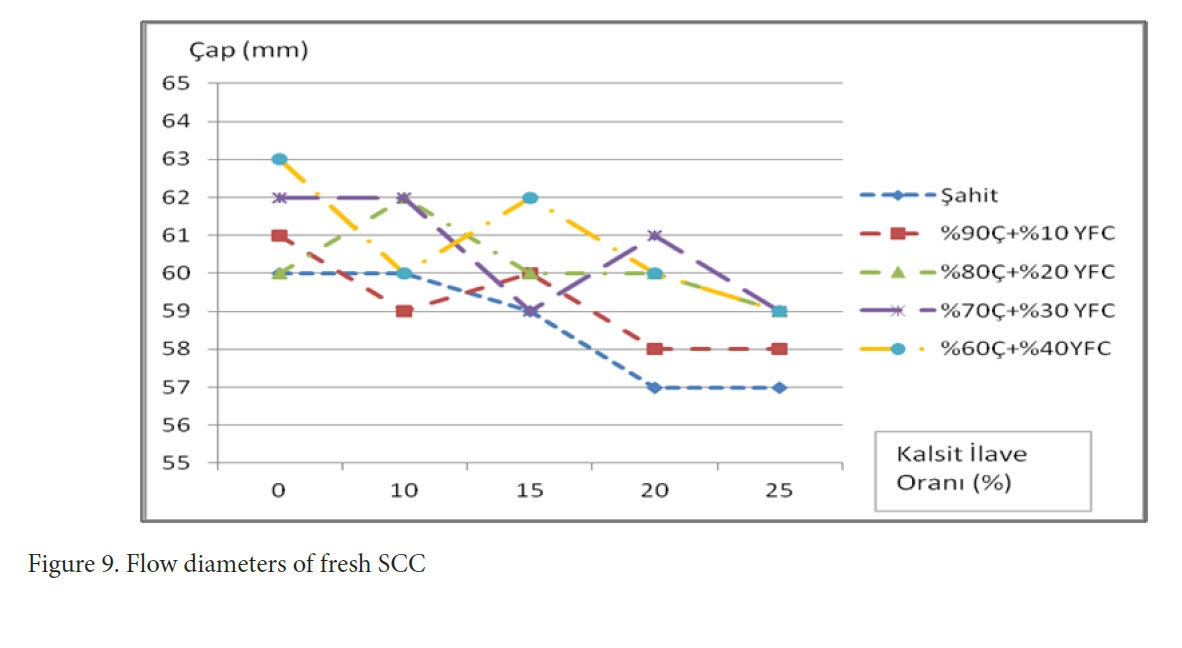
Figure 9

Figure 10

Figure 11
Physicalproperties |
Fine aggregate |
Coarse aggregate |
|
Sieve range |
0-4 mm |
4-12 mm |
12-22 mm |
Density (g/cm3) |
2.60 |
2.63 |
2.65 |
Water absorption (%) |
1.50 |
0.75 |
0.25 |
Table1 Physical properties of aggregates
Aggregate |
Last percentage (%) |
|||||||||
0.125 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
16 |
22 |
32 |
|
0-4 mm |
9 |
21 |
33 |
60 |
83 |
99 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
4-12 mm |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
12 |
93 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
12-22 mm |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
10 |
73 |
100 |
Table2 Aggregate sieve analysis
Properties |
Polycarboxylate |
Density (g/cm3) |
1,06 |
pH |
5,6 |
Drymaterialcontent(%) |
25 |
Table3 Physical properties of chemical additives
Kimyasal özellikler |
SiO2 |
Al2O3 |
Fe2O3 |
CaO |
MgO |
Na2O |
K2O |
SO3 |
(%) |
21.16 |
4.05 |
2.26 |
63.7 |
1.30 |
0.30 |
0.35 |
3.30 |
Table4 Chemical properties of CEM I cement
Materials |
Material Amount (g) |
|||||||||||||||
Cement (g) |
1000 |
1000 |
1000 |
1000 |
||||||||||||
Water (g) |
330 |
330 |
330 |
330 |
||||||||||||
Calcite (%) |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
||||||||||||
BFS (%) |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
Additive (g) |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
||||||||||||
Table15 Paste mixture amounts
Materials |
Material Amount (g) (kg/m3) |
||||||||||||||||
Cement |
350 |
315 |
280 |
245 |
210 |
||||||||||||
0-4 aggregate |
1000 |
965 |
930 |
895 |
860 |
||||||||||||
4-12 aggregate |
290 |
290 |
290 |
290 |
290 |
||||||||||||
12-22 aggregate |
570 |
570 |
570 |
570 |
570 |
||||||||||||
Water |
175 |
175 |
175 |
175 |
175 |
||||||||||||
Calcite (%10,15,20,25) |
0 |
35 |
52,5 |
70 |
87,5 |
35 |
52,5 |
70 |
87,5 |
35 |
52,5 |
70 |
87,5 |
35 |
52,5 |
70 |
87,5 |
BFS (%10,20,30,40) |
0 |
35 |
70 |
105 |
140 |
||||||||||||
|
3,5 |
3,5 |
3,5 |
3,5 |
3,5 |
||||||||||||
Theoretical unit weight |
2388,5 |
2388,5 |
2388,5 |
2388,5 |
2388,5 |
||||||||||||
Water/cement ratio |
0,50 |
0,50 |
0,50 |
0,50 |
0,50 |
||||||||||||
Table6 shows, the amount of mixture of SCC in 1 cubic meter is given