Sample name |
Eg (eV) |
-1 |
MB |
-- |
4*10-8 |
Z |
3.20 |
0.0014 |
MZ |
2.07 |
0.0112 |
MZT |
1.90 |
0.02317 |
MZR |
1.89 |
0.0359 |
Table 1: The band gap energy (Eg) values and kinetic parameters for photocatalytic activities of Z, MZ, MZT, and MZR NCs
Photocatalyst |
Weight of catalyst (g/L) |
Concentration of MB (ppm) |
Time(h) |
Degradation (%) |
Ref. |
ZnS-TiO2/RGO |
0.4 |
20 |
2 |
90 |
[56] |
WO3/GO |
0.5 |
3 |
1.2 |
82 |
[57] |
Pt/WO3/GO |
0.5 |
3 |
1.2 |
94 |
[57] |
Fe3O4 /CdWO4 +H2O2 |
0.1 |
20 |
2 |
32 |
[58] |
Fe3O4 /CdWO4 /PrVO4 + H2O2 |
0.1 |
20 |
2 |
68 |
[58] |
Fe3O4/ZnWO4/CeVO4 +H2O2 |
0.6 |
25 |
2 |
84 |
[59] |
Pt/ZnO-MWCNT |
0.4 |
100 |
1 |
74 |
[60] |
MZG3 |
2 |
100 |
1.5 |
95 |
Our work |
Table 2: Photocatalytic degradation of MB under Visible Light with Various Photocatalysts


Scheme 1: Schematic Synthesis of Fe3O4 /ZnO/ rGO nanocomposites (MZR)

Scheme 2: Schematic Synthesis of Fe3O4 / ZnO /TiO2 nanocomposites (MZT)
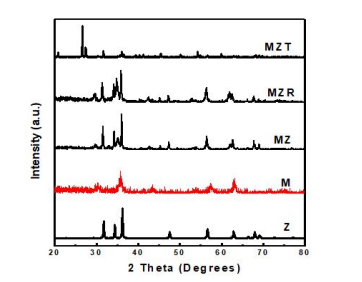
Figure 1: XRD spectra of Z, M, MZ, MZR and MZT nanocomposites
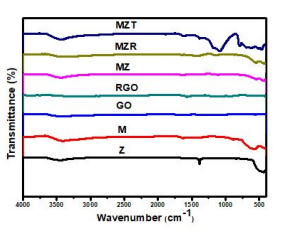
Figure 2: FT-IR spectra of Z, M, MZ, MZR, and MZT nanocomposites
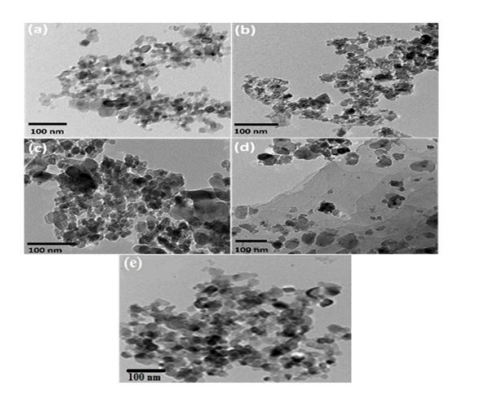
Figure 3: TEM images of Z (a), M (b), MZ (c), MZR (d) and MZT(e)
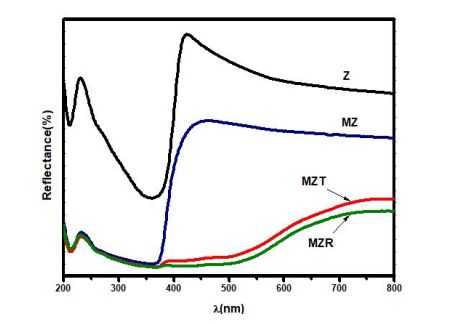
Figure 4: UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of Z, MZ, MZT and MZR NCs
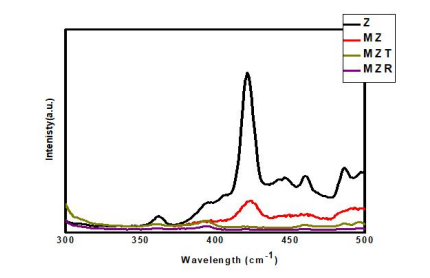
Figure 5: Photoluminescence spectra of Z, MZ, MZT and MZR NCs
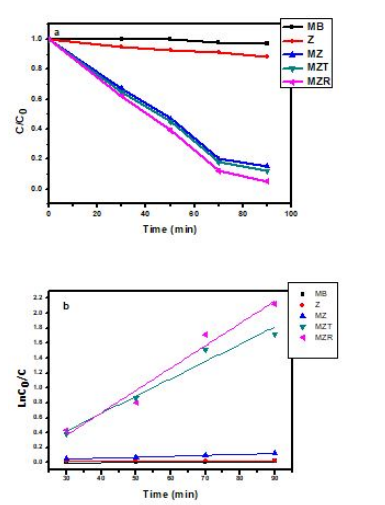
Figure 6: Photodegradation and (b) Kinetic of MB by Z, MZ, MZT and MZR nanocomposites for 100 ppm MB under visible light
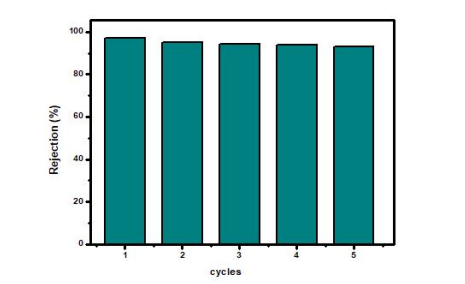
Figure 7: The MZR photocatalytic activity for degradation of organic pollutant remained stable (about 95%) throughout five consecutive cycles
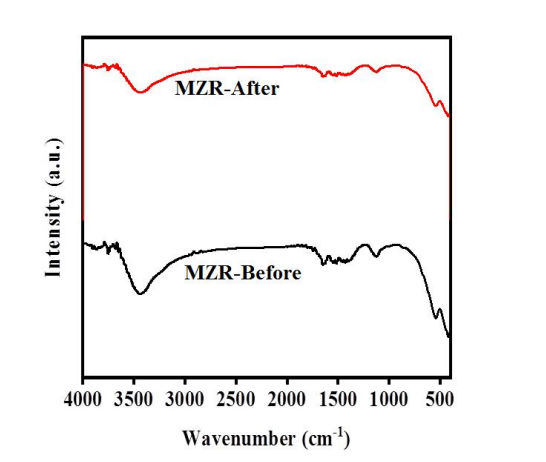
Figure 8: FT-IR spectra of MZR nanocomposites before and after of photocatalytic activity
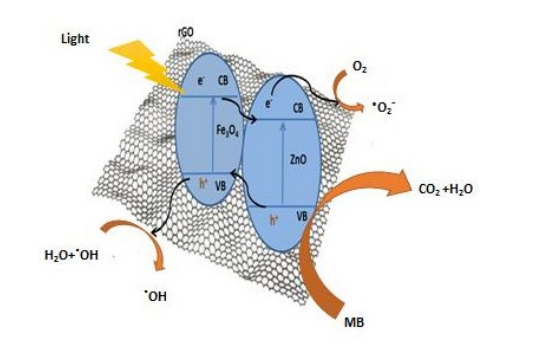
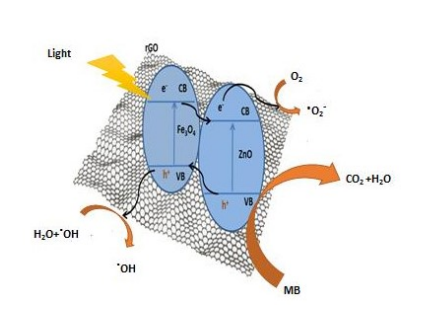
Figure 9: Schematic diagram of MB photodegradation by MZR crystalline nanocomposite under visible light
Tables at a glance
Figures at a glance