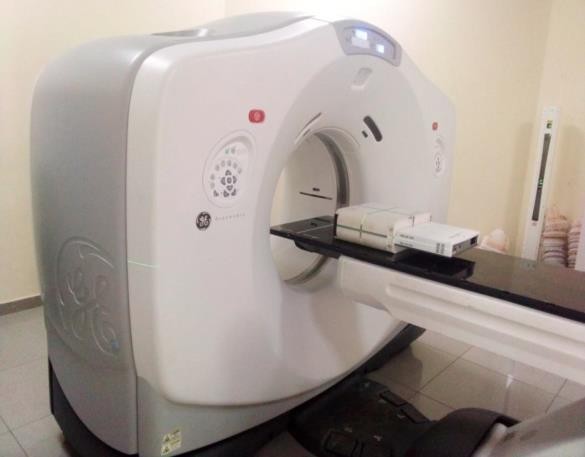
Figure 1: CT scanning of the miniPhantom with the MatriXX 2D array detector embedded in it
Head and Neck |
Prostate |
||
Critical organ |
Dose (EQD2)/ Volume |
Critical organ |
Dose (EQD2)/ Volume |
Brain |
V60 Gy ≤ 30 % |
Small Bowel |
Dmax = 46 Gy Daverage ≤ 30 Gy |
Lens |
Dmax = 4 Gy |
||
Eye |
Dmax = 45 Gy |
Rectum |
V50Gy ≤ 50 % V60Gy ≤ 40 % |
Esophagus and Lacrimal gland |
Daverage ≤ 34 Gy |
||
Chiasm and Optical nerve |
V54Gy ≤ 2 % |
Bladder |
Daverage ≤ 62 Gy |
Cochlea |
Daverage ≤ 40 Gy |
Penile bulb |
Daverage ≤ 50 Gy |
Brain stem |
V60Gy ≤ 2 % |
Testicle |
Dmax = 8 Gy |
Spinal cord |
Dmax = 48 Gy |
Ovaries |
Dmax = 2 Gy |
Parotid gland |
Daverage ≤ 26 Gy |
Femoral head |
Dmax = 55 Gy |
Larynx |
V50Gy ≤ 30 % |
Sacrum |
Daverage ≤ 50 Gy |
Table 1 : Dose Volume Objectives/ Constraints to critical organs
Case |
Patient |
Dose (Gy) |
Percentage dose difference (%) |
||
TPS calculated |
Measured |
Difference |
|||
Prostate |
1 |
3.08 |
3.07 |
0.01 |
0.43 |
2 |
3.08 |
3.06 |
0.03 |
0.90 |
|
3 |
4.47 |
4.46 |
0.01 |
0.16 |
|
4 |
3.37 |
3.34 |
0.02 |
0.70 |
|
5 |
2.58 |
2.58 |
0.00 |
0.17 |
|
Head-and-neck |
6 |
2.72 |
2.73 |
0.01 |
0.24 |
7 |
2.85 |
2.85 |
0.00 |
0.16 |
|
8 |
3.41 |
3.40 |
0.01 |
0.36 |
|
9 |
2.24 |
2.22 |
0.02 |
0.71 |
|
10 |
3.11 |
3.11 |
0.00 |
0.07 |
|
Table 2: Comparison of ionization chamber measured and TPS calculated doses for the IMRT plans
Case |
Patient |
Pass rates (%) |
|||
1st verification |
2nd verification |
3rd verification |
Mean ± SD |
||
Prostate |
1 |
97.50 |
97.20 |
98.10 |
97.60 ± 0.46 |
2 |
95.40 |
95.40 |
96.60 |
95.80 ± 0.69 |
|
3 |
96.10 |
96.80 |
97.40 |
96.77 ± 0.65 |
|
4 |
98.30 |
97.90 |
99.10 |
98.43 ± 0.61 |
|
5 |
95.40 |
96.00 |
95.10 |
95.50 ± 0.46 |
|
Head-and-neck |
6 |
93.70 |
95.00 |
95.10 |
94.60 ± 0.78 |
7 |
96.50 |
96.90 |
96.90 |
96.77 ± 0.23 |
|
8 |
96.50 |
97.10 |
96.80 |
96.80 ± 0.30 |
|
9 |
96.30 |
95.80 |
96.60 |
96.23 ± 0.40 |
|
10 |
97.10 |
97.80 |
98.20 |
97.70 ± 0.56 |
|
Table 3: Gamma passing rates for the various IMRT plans and different verifications

Figure 1: CT scanning of the miniPhantom with the MatriXX 2D array detector embedded in it
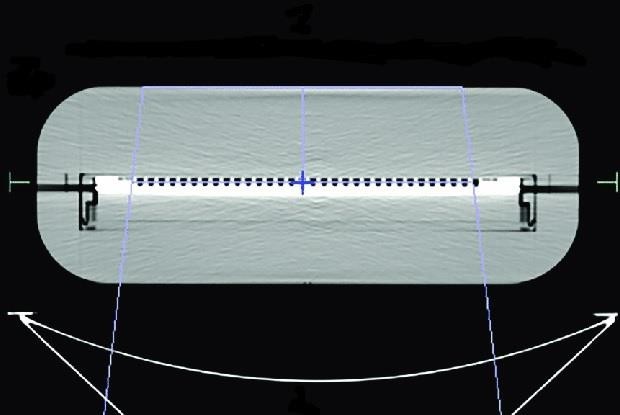
Figure 2: Axial CT slice of the miniPhantom and 2D array detector
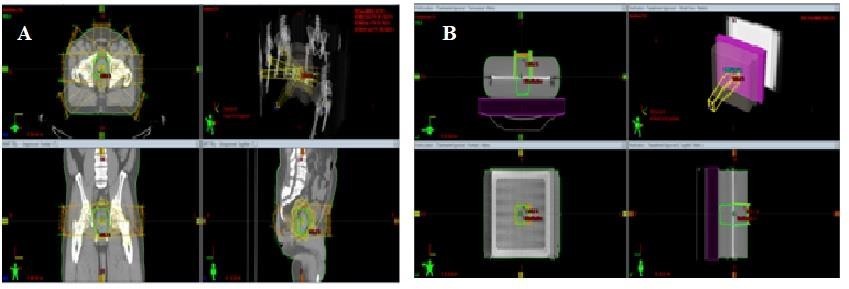
Figure 3: TPS planning window: A. prostate IMRT plan, B. Verification plan
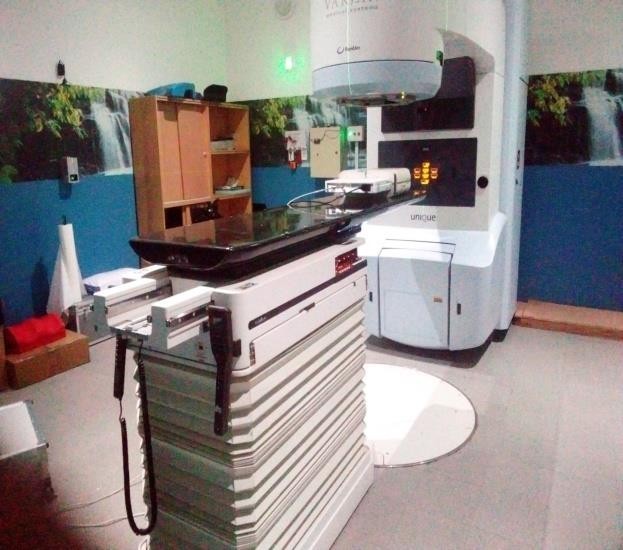

Figure 4: Treatment delivery with the miniPhantom having the MatriXX detector inserted into the phantom
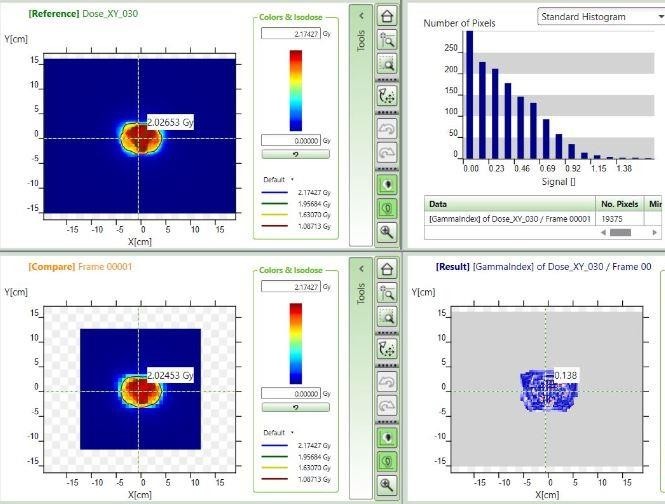
Figure 5: Dose comparison window of myQA software
Figure 6(a): Gamma passing rates of IMRT plans for (a) prostate
Figure 6(b): Gamma passing rates of IMRT plans for (b) head-and-neck cases
Tables at a glance
Figures at a glance