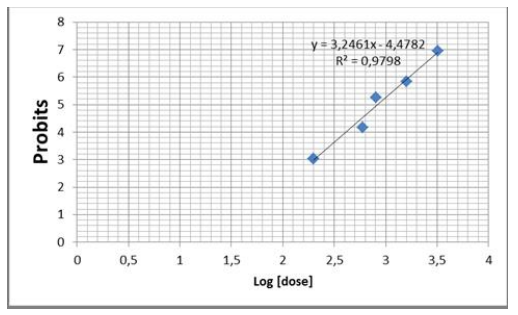
Figure 1: Plot of log dose of aqueous leaf extract of Cistus ladaniferus vs probit mortality values using probit analysis
Phytochemical |
Extract |
Flavonoïdes |
++ |
Tannins |
++ |
Stérolsettriterpènes |
- |
Quinones |
- |
Saponines |
+ |
Alcaloïdes |
- |
Table 1: Result of qualitative phytochemical composition of C. ladaniferus (L) extract
Bioavailability key; – = not detected, + = present in low concentration, ++ = present in moderately high concentration
|
Control |
200mg/kg |
400mg/kg |
600mg/kg |
800mg/kg |
3200mg/kg |
Respiration |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Change |
Food intake |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Change |
Immobility |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Lethargy |
Rigidity of the hind limbs |
NP |
NP |
NP |
NP |
P |
P |
Body weight |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Change |
Change in skin |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
N.O |
Eyes |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N.O |
Table 2: Evaluation of the clinical signs of the aqueous leaf extract of C. ladaniferus intraperitoneally administered to mice
N= normal, N.P= not present, P= present, N.C= not change, NO= not observed
These signs disappeared after 48 hours. And at the end of the test, all the surviving mice return to their normal state.
Doses(mg/kg) |
wek1 |
wek2 |
wek3 |
wek4 |
wek5 |
wek6 |
wek7 |
wek8 |
wek9 |
wek10 |
wek11 |
wek12 |
0 |
170.1±27.2 |
178,22±27.2 |
181.7±26.6 |
184.9±27.2 |
189.7±27.2 |
194.5±25.4 |
198.9±27.2 |
200.1±27.2 |
201.2±27.2 |
202.8±27.2 |
203.5±29.2 |
202.8±27.2 |
500 |
209.2±30.2 |
218.1±20.2 |
230.9±28.9 |
238.7±25.1 |
246.1±30.2 |
250.2±26.1 |
252.6±15.3 |
256.2±26.6 |
259.1±29.2 |
259.7±26.1 |
260.3±28.8 |
260.12±28.5 |
1500 |
196.8±28.2 |
221.32±28.2 |
224.3±26.1 |
226.34±26.2 |
229.2±26.2 |
230.2±26.9 |
234.7±32.2 |
236.1±27.2 |
236.7±20.2 |
238.0±28.2 |
239.9±32.0 |
235.0±28.2 |
Table 3: Effect of oral administration of the aqueous leaf extract of C. ladaniferus on the weight of rats
|
Liver |
Kidneys |
Spleen |
Control mg/kg |
7.20 ±0.7 |
0.61±0.02 |
0.51.±0.04 |
500mg/kg |
6.87±0.30 |
0.62±0.02 |
0.53±0.05 |
1500mg/kg |
6.67±0.19 |
0.59±0.03 |
0.50±0.03 |
Table 4: Organ weights (g) of the rats in the sub-chronic toxicity studies of the aqueous leaf extract of C. ladaniferus . n = 8, Values are ex- pressed as mean ± SEM, * p >0,05
The values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of 8 rats in each group. Group I: Control (0 mg / kg); Group II: 500 mg / kg; Group III: 1500 mg / kg.
Parameters |
Doses (mg/kg) |
||
Control |
500 |
1500 |
|
Red blood cells (106/µl) |
7,70±0,53 |
7,71 ±0.20* |
7,93±0,40 * |
White blood cells (103/µl) |
9,10± 0,51 |
9,08± 0,15 * |
8,95±0,59 * |
Haemoglobin (g/dl) |
15,89± 0,85 |
15,43± 0,69 * |
15,66 ±0,62 * |
Hématocrit (vol %) |
40,87 ±0,45 |
41,75±0,66 * |
41,62±0,8 * |
Platelets (104/µl) |
70,97± 0,86 |
70,74±0,8 4* |
70,99±0,74 * |
Table 5: Study of the haematological parameters of rats after daily oral administration of the aqueous leaf extract of C. ladaniferus for 90 days. n = 8, Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, * p >0,05
Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of 8 rats in each group.Group I: Control (0 mg / kg); Group II: 500 mg / kg; Group III: 1500 mg / kg.
Parameters |
Doses (mg/kg) |
||
Control |
500 |
1500 |
|
Creatinine (µmol/l) |
59±0.91 |
60,4±0.20 * |
61,4±0.55 * |
ASAT (U/L) |
83,5± 6,52 |
80,1±6,56 * |
84,75±3,19 * |
ALAT (U/L) |
22,1± 3,87 |
23,2± 1,28 * |
23,5±1,30 * |
Total protein (g/l) |
82,01±7,41 |
84,2±7,25 * |
82,2±7,48 * |
Table 6: Study of the biochemical parameters of rats after daily oral administration of the aqueous leafextractof C. ladaniferus . n = 8, Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, * p >0,05
Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of 8 rats in each group. Group I: Control (0 mg / kg); Group II: 500 mg / kg; Group III: 1500 mg / kg.

Figure 1: Plot of log dose of aqueous leaf extract of Cistus ladaniferus vs probit mortality values using probit analysis
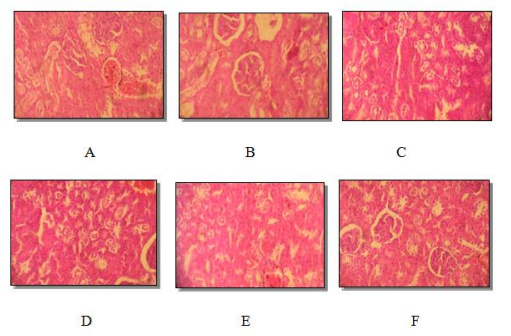
Figure 2: Histological section of male rat kidney (A) and female rat (B) control. Male rat (C) and female rat (D) treated (dose of 500mg / kg). Male rat (E) and female rat (F) treated (dose of 1500mg / kg). Vascular congestion. Hematoxylin Eosin Stain (Average magnification)
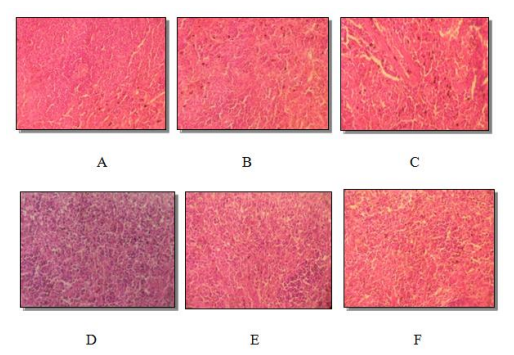
Figure 3: Histological section of male rat spleen (A) and female rat (B) controls. Male rat (C) and female rat (D) rats treated (500 mg / kg dose) treated male rat (E) and female rat (F) rats (dose of 1500 mg / kg). Eosin hematoxylin staining. (Average magnification)
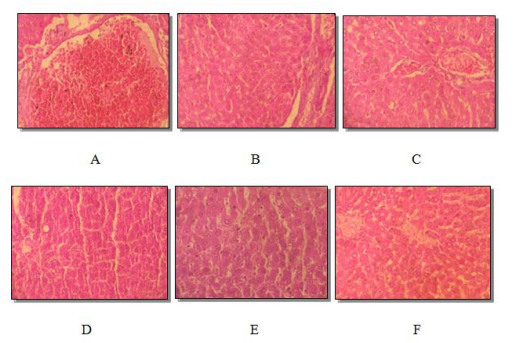
Figure 4: Histological section of male rat liver (A) and female rat (B) controls. Male rat (C) and female rat (D) treated (dose of 500mg / kg). Male rat (E) and female rat (F) treated (dose of 1500mg / kg). Eosin hematoxylin staining. (Average magnification)
Tables at a glance
Figures at a glance